Functional state of cardiovascular system in children, living permanently on the radiocontaminated territories
The objective of the present research consisted in studying the functional state of cardiovascular system in children, living permanently on the radiocontaminated territories.
Tasks:
1. To study complaints and anamnesis of children, living on the radiocontaminated territories and to trace the dependence of revealed modifications from the Cesium-137 specific activity in children.
2. To analyze ECG modifications and modifications of arterial pressure, as basic indications of the functional state of cardiovascular system, depending on the level of the Cesium-137-accumulation in the organism.
3. To trace the dynamics of ECG-modifications before and after taking the food additive “Vitapect”.
Materials and methods:
We examined 94 children, including 46 boys and 48 girls from 7 to 17, from contaminated districts of the Gomel region, who was on rehabilitation in the sanatorium “Serebryanye Klyuchi” of the Svetlogorsk district. The measurements of the internal Cesium-137 accumulation in children were performed with the help of the automated complex for spectrometry of human internal radiation “SKRINNER-3M”.
The standardized protocol of the clinical investigation consisted of complaints and anamnesis of the child’s life, the pediatric checkup, the performance of functional loading probes and the ECG-examinations. All children were examined two times with an interval of 16 days (before and after pectin cures).
Depending on the Cesium-137-concentration in the organism, all examined children were divided into three groups:
The first group consisted of 31 children with the average Cesium-137 specific activity in the organism of 38 ± 2.4 Bq/kg,
the second group consisted of 30 children with the average Cesium-137 activity in the organism of 122 ± 18.5 Bq/kg.
The control group consisted of 33 children, which had not Cesium-137 in their organism and needed the sorption therapy. The groups were not differentiated on children’s age and sex.
During 16 days all children of the basic group received the food additive “Vitapect”, in order to remove Cesium-137 from the organism. After that the Cesium-137 specific activity in children of the first and second group reached 23 ± 2,5 Bq/kg and 88 ± 18,5 Bq/kg (Fig. No 3).
Results and discussions:
The general number of cardiac (whined pains in heart) and extracardiac (headaches, weakness, irritability, nasal bleedings) complaints during the primary examination of the control and two basic groups of children had differences: 10 (30.3%); 12 (38.7%); 19 (63.4%).
The number of complaints, basically of asthenoneurotic kind, prevailed reliably in children of the second basic group in comparison with the control group 10 (30.3%).
When analyzing the anamnestetic data of children’s food it was detected, that 22 (71%) of 30 children (100%) of the second basic group ate foodstuffs from private farms (milk, meat) and product from forest (berries, mushrooms, game). In the control; group these foodstuffs were used by 19 children (57.6%) (Table 1).
Table 1
Distribution of the data of anamnesis of food of the examined children in the basic and control groups
|
No |
Data of anamnesis of children’s food |
Basic group |
Control group |
|
|
1st group |
2nd group |
|||
|
1 |
Milk and products from forest |
19 (61,3%) |
29 (96,7%) |
10 (30,3%) |
|
2 |
Foodstuffs from private farms (milk, meat) |
1 (3,2%) |
1 (3,3%) |
5 (15,2%) |
|
3 |
Products from forest (berries, mushrooms, game) |
2 (6,5%) |
- |
4 (12,1%) |
|
4 |
Do not eat the foodstuffs, mentioned above |
9 (29%) |
- |
14 (42,4%) |
|
|
A total of |
31 |
30 |
33 |
According to the data of the auscultative examination of heart the presence of the functional systolic noise and systolic clicks at the top of heart in 26 children (83.8%) of the first group and 26 children (86.7%) of the second group of the basic group and in 16 children (48.5%) of the control group was diagnosed.
Clean, loud tones prevailed in 17 children (51.5%) from the control group in comparison with 5 children (16.2%) of the first and with 4 children (13.3%) of the second groups of the basic group (Table 2).
Table 2
Frequency of auscultative modifications in children os the basic and control groups
|
№ п/п |
Auscultative data
|
Basic group |
Control group N=33 |
|
1st group n=31 |
2nd groupn=30 |
|||
|
1 |
Functional systolic noise |
18 (58,0%) |
22 (73,4%) |
12 (36,4%) |
|
2 |
Noise of systolic click |
8 (25,8%) |
4 (13,3%) |
4 (12,1%) |
|
3 |
Clean, loud tones |
5 (16,2%) |
4 (13,3%) |
17 (51,9%) |
The level of arterial pressure is a basic indication of the functional state of cardiovascular system. When performing functional loading probes the reliable increase of the hypertonic type of vascular reaction to the physical load in 8 children (25.8%) of the first group and 15 children (50%) of the second group of the basic group and in 3 children (9.1%) of the control group (Table 3, fig. 4).
Table 3
Type of vascular reaction to the load in children
|
No |
Type of vascular reaction |
Basic group |
Control group n=33 |
|
1st groupn=31 |
2nd groupn=30 |
|||
|
1 |
Normotonic |
21 (67,7%) |
12 (40%) |
28 (84,8%) |
|
2 |
Hypertonic |
8 (25,8%) |
15 (50%) |
3 (9,1%) |
|
3 |
Asthenic |
2 (6,5%) |
3 (10%) |
2 (6,1%) |
In children of the first and second groups and control groups ECG-modifications were accordingly found in 25 (87.1%), 28 (93.4%) and 17 (51.5%).
The present modifications are disorder of conduction (partial bundle branch blockade) and combined modifications (disorder of metabolic processes in myocardium and partial bundle branch blockade).
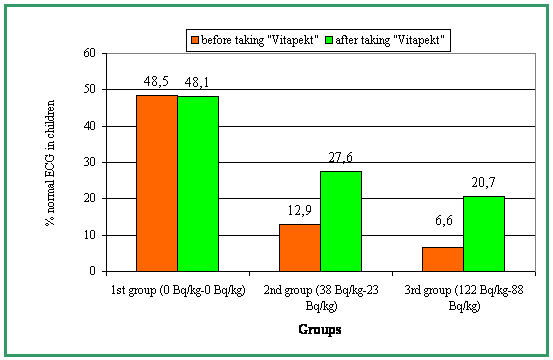
4 children (12.9%) of the first group, 2 children (6.6%) of the second basic groups and 16 children (48.5%) of the control group had the normal ECG-results (fig. 1, 2). The dependence of ECG-modifications on the average Cesium-137 specific activity in children’s organism was detected.
After taking pectin, containing sorbent, there was the reliable decrease of the frequency of metabolic processes in myocardium in combined pathology in children from the first basic group from 7 (25.9%) before taking pectins and 2 (9.5%) after taking pectins (fig. 2). In children from the second basic group the present modifications before and after taking pectins such modifications were accordingly found in 14 (50%) and 4 (17.4%). In the control group there were no reliable differences, because they did not receive the sorption pectin therapy. (table 4 and fig.5).
Table 4
Dynamics of ECG-modifications in children after taking pectins
|
No |
ECG-modifications |
Basic group |
Control group |
||||
|
1st group |
2nd group |
||||||
|
|
|
Before pectin n=31 |
After Pectin n=29 |
Before pectin n=30 |
After Pectin n=29 |
Before pectin n=33 |
After pectin n=27 |
|
1 |
Disorders of automatism |
4 (14,8%) |
3 (14,3%) |
1 (3,6%) |
2 (8,7%) |
- |
2 (14,3%) |
|
2 |
Disorders of conduction |
13 (48,1%) |
12 (51,1%) |
9 (32,1%) |
13 (56,5%) |
13 (76,5%) |
11 (78,6%) |
|
3 |
Disorders of oxidizing-restoring processes |
3 (11,1%) |
4 (19,%) |
4 (14,3%) |
4 (17,4%) |
4 (23,5%) |
1 (7,1%) |
|
4 |
Combined pathologies |
7 (25,9%) |
2 (9,5%) |
14 (50%) |
4 (17,4%) |
- |
- |
|
5 |
Normal ECG |
4 (12,9%) |
8 (27,6%) |
2 (6,6%) |
6 (20,7%) |
16 (48,5%) |
13 (48,1%) |
1. Children, living in villages and eating foodstuffs, produced there, and products from forests, have the high Cesium concentration in the organism.
2. Children from contaminated districts have functional modifications of the state of cardiovascular system, which appear as systolic noise, high arterial pressure, ECG-modifications in heart.
3. Presences of systolic noise, high arterial pressure and ECG-modifications in children’s heart are in dose dependence from the level of the Cesium-137 accumulation in the organism.
4. The use of pectins improves electrophysiological processes in myocardium, due to the decrease of metabolic processes on ECG.
Figure 1. Dynamics of normal ECG in children, depending on the average Cesium-137 level in the organism before and after taking the food additive “Vitapect-2”

Figure 2. Dynamics of ECG-modifications in children, depending on the average Cesium-137 level in the organism before and after taking the food additive “Vitapect-2”

xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Figure 3. Dynamics of the average Cesium-137 specific activity, when taking the food additive “Vitapect”

Figure 4. Modification, like vascular reaction to the load, depending on the average Cesium-137 specific activty

Figure 5. Dynamics of ECG in children depending on the average Cesium-137 specific activty, when taking “Vitapect”

А – control group of children with the Cesium-137 specific activity of 0 Bq/kg
during the first measurement.B – control group of children with the Cesium-137 specific activity of 0 Bq/kg
during the second measurement.C – group of children before taking “Vitapect” (the Cesium-137 specific activity of 38 Bq/kg).
D – group of children before taking “Vitapect” (the Cesium-137 specific activity of 23 Bq/kg).
E – group of children before taking “Vitapect” (the Cesium-137 specific activity of 122 Bq/kg).
F – group of children before taking “Vitapect” (the Cesium-137 specific activity of 88 Bq/kg).

Source: W.T.